Build a Slackbot
Before you start
All of the tutorials assume you have already completed the Get started guide, which gets you set up with a Cloudflare Workers account, and the Workers CLI tool, Wrangler.
Overview
In this tutorial, you will build a Slack bot using Cloudflare Workers. Your bot will make use of GitHub webhooks to send messages to a Slack channel when issues are updated or created, and allow users to write a command to look up GitHub issues from inside Slack.
This tutorial is recommended for people who are familiar with writing web applications. If you have built an application with tools like Node and Express, this project will feel very familiar to you. If you are new to writing web applications or have wanted to build something like a Slack bot in the past, but were intimidated by deployment or configuration, Workers will be an easy way for you to focus on writing code and shipping projects.
If you would like to review the code or how the bot works in an actual Slack channel before proceeding with this tutorial, you can access the final version of the codebase on GitHub. From GitHub, you can add your own Slack API keys and deploy it to your own Slack channels for testing.
Set up Slack
This tutorial assumes that you already have a Slack account, and the ability to create and manage Slack applications.
Configure a Slack application
To post messages from your Cloudflare Worker into a Slack channel, you will need to create an application in Slack’s UI. To do this, go to Slack’s API section, at api.slack.com/apps, and select Create New App.
Slack applications have many features. You will make use of two of them, Incoming Webhooks and Slash Commands, to build your Worker-powered Slack bot.
Incoming Webhook
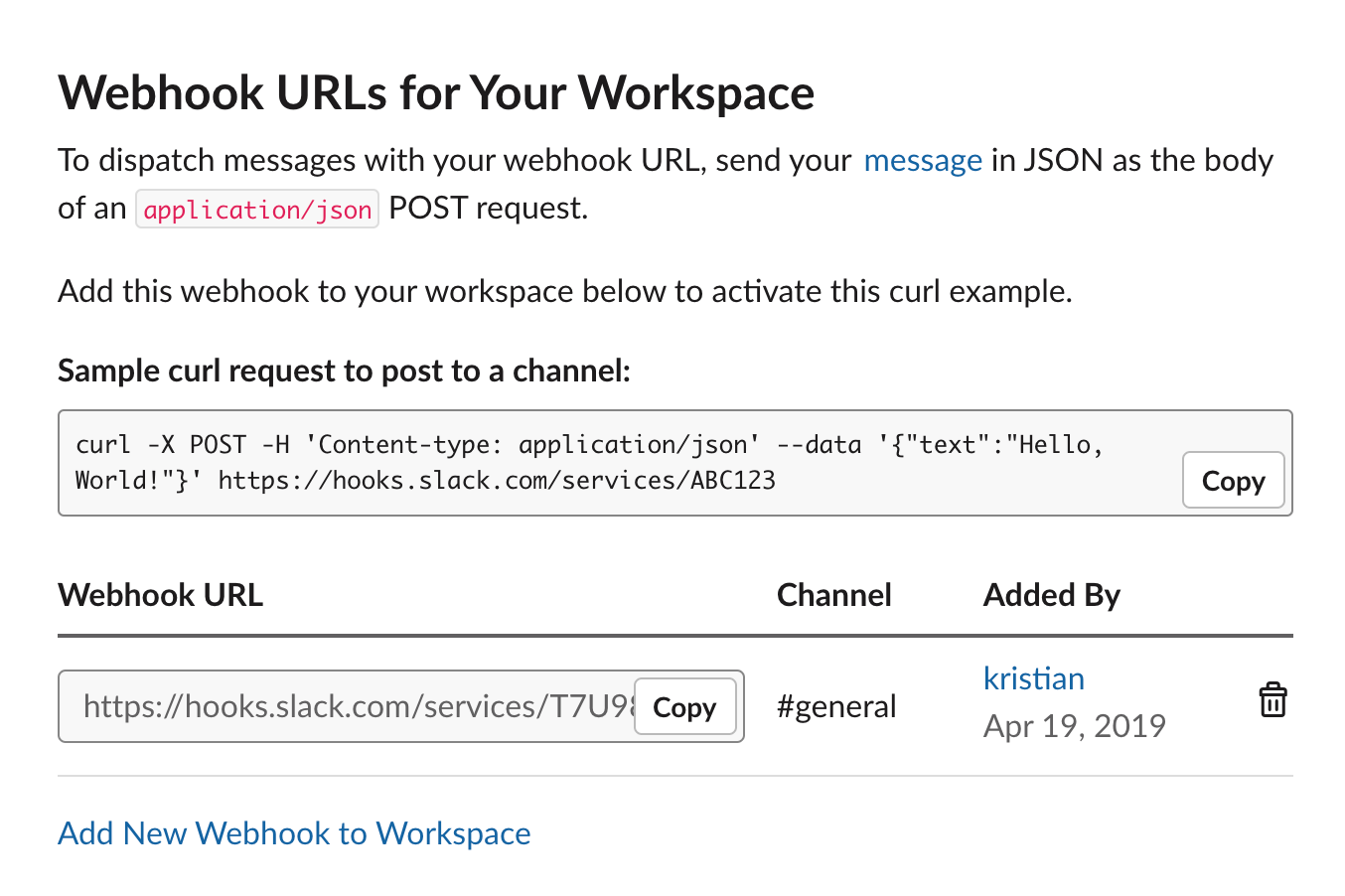
Incoming Webhooks are URLs that you can use to send messages to your Slack channels. Your incoming webhook will be paired with GitHub’s webhook support to send messages to a Slack channel whenever there are updates to issues in a given repository. You will see the code in more detail as you build your application. First, create a Slack webhook:
- On the sidebar of Slack’s UI, select Incoming Webhooks.
- In Webhook URLs for your Workspace, select Add New Webhook to Workspace.
- On the following screen, select the channel that you want your webhook to send messages to (you can select a room, like #general or #code, or be messaged directly by your Slack bot when the webhook is called.)
- Authorize the new webhook URL.
After authorizing your webhook URL, you will be returned to the Incoming Webhooks page and can view your new webhook URL. You will add this into your Workers code later. Next, you will add the second component to your Slack bot: a Slash Command.
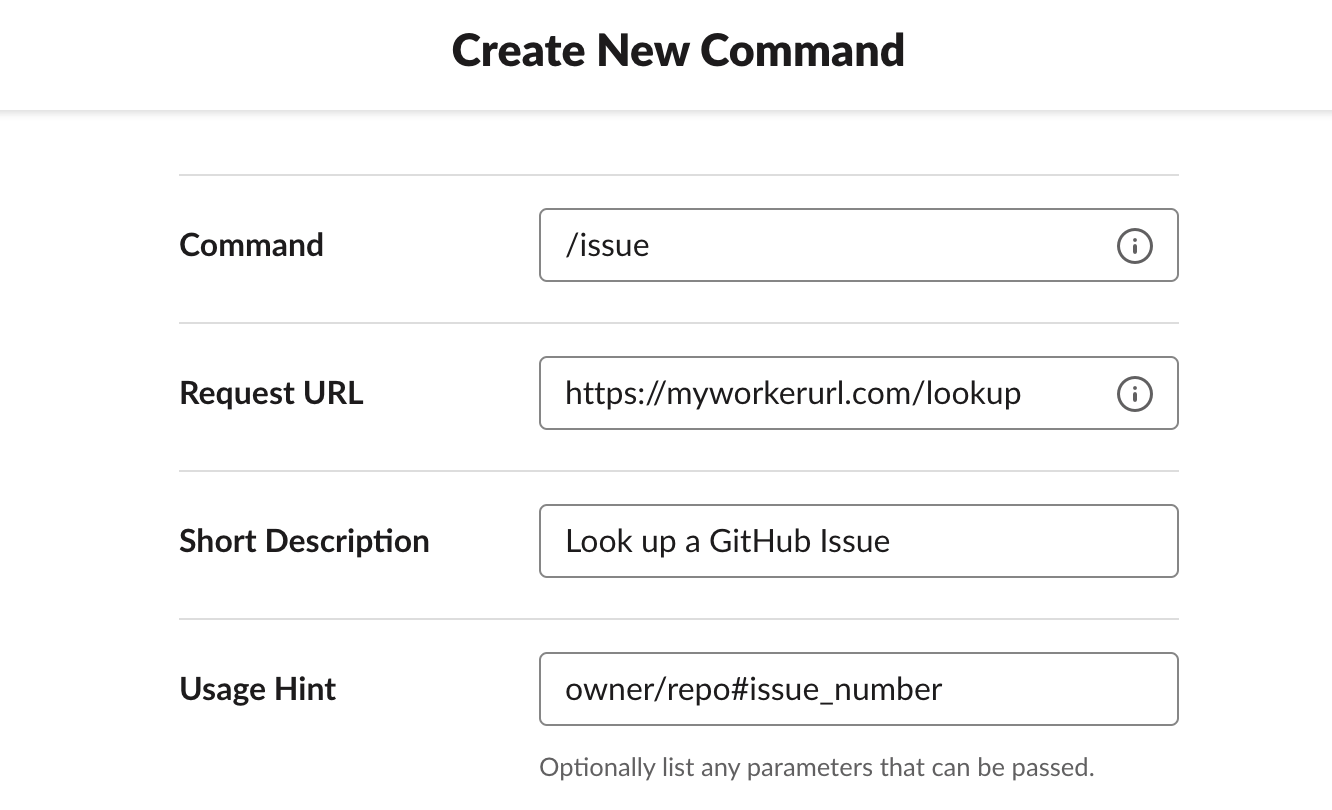
Slash Command
A Slash Command in Slack is a custom-configured command that can be attached to a URL request. For example, if you configured /weather <zip>, Slack would make an HTTP POST request to a configured URL, passing the text <zip> to get the weather for a specified zip code. In your application, you will use the /issue command to look up GitHub issues using the GitHub API. Typing /issue cloudflare/wrangler#1 will send the text cloudflare/wrangler#1 in a HTTP POST request to your application, which the application will use to find the relevant GitHub issue.
- On the Slack sidebar, select Slash Commands.
- Create your first slash command.
For this tutorial, you will use the command /issue. The request URL should be the /lookup path on your application URL: for example, if your application will be hosted at https://myworkerurl.com, the Request URL should be https://myworkerurl.com/lookup.
Configure your GitHub Webhooks
Your Cloudflare Workers application will be able to handle incoming requests from Slack. It should also be able to receive events directly from GitHub. If a Github issue is created or updated, you can make use of GitHub webhooks to send that event to your Workers application and post a corresponding message in Slack.
To configure a webhook:
- Go to your Github repository’s Settings > Webhooks > Add webhook.
If you have a repository like https://github.com/user/repo, you can access the Webhooks page directly at https://github.com/user/repo/settings/hooks.
- Set the Payload URL to the
/webhookpath on your Worker URL.
For example, if your Worker will be hosted at https://myworkerurl.com, the Payload URL should be https://myworkerurl.com/webhook.
- In the Content type dropdown, select application/json.
The Content type for your payload can either be a URL-encoded payload (application/x-www-form-urlencoded) or JSON (application/json). For the purpose of this tutorial and to make parsing the payload sent to your application, select JSON.
- In Which events would you like to trigger this webhook?, select Let me select individual events.
GitHub webhooks allow you to specify which events you would like to have sent to your webhook. By default, the webhook will send push events from your repository. For the purpose of this tutorial, you will choose Let me select individual events.
- Select the Issues event type.
There are many different event types that can be enabled for your webhook. Selecting Issues will send every issue-related event to your webhook, including when issues are opened, edited, deleted, and more. If you would like to expand your Slack bot application in the future, you can select more of these events after the tutorial.
- Select Add webhook.
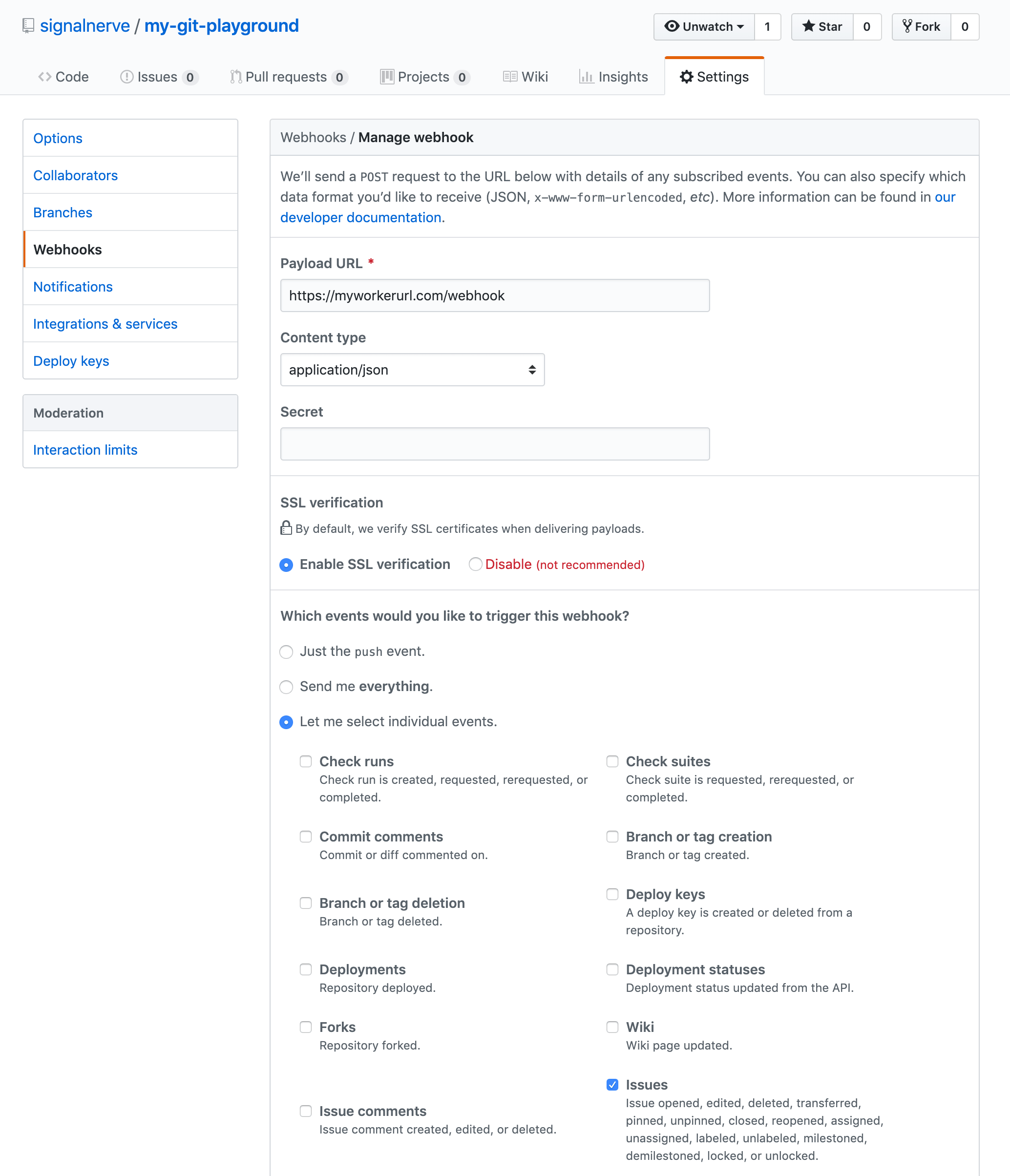
When your webhook is created, it will attempt to send a test payload to your application. Since your application is not actually deployed yet, leave the configuration as it is. You will later return to your repository to create, edit, and close some issues to ensure that the webhook is working once your application is deployed.
Init
Cloudflare’s command-line tool for managing Worker projects, Wrangler, supports various templates — pre-built collections of code that make it easy to get started writing Workers. In this tutorial, you will use the router template to create a Workers project with a built-in router, so you can take incoming requests, and route them to the appropriate JavaScript code.
In the command line, create your Worker project, cloning the router template URL and passing in a project name (for example, slack-bot):
Create a new project$ git clone https://github.com/cloudflare/worker-template-router slack-bot
$ cd slack-bot
Wrangler templates are just Git repositories, so if you want to create your own templates, or use one from the Template Gallery, there is a variety of options to help you get started.
Cloudflare’s worker-template includes support for building and deploying JavaScript-based projects. Inside of your new slack-bot directory, index.js represents the entry point to your Cloudflare Workers application.
All Cloudflare Workers applications start by listening for fetch events, which are triggered when a client makes a request to a Workers route. After a request is received by the Worker, the response your application constructs will be returned to the user. This tutorial will guide you through understanding how the request/response pattern works and how you can use it to build fully featured applications.
index.jsaddEventListener('fetch', event => { event.respondWith(handleRequest(event.request));
});
/** * Handle a request * @param {Request} request */
async function handleRequest(request) { return new Response('Hello worker!', { status: 200 });
}
In your default index.js file, you can see that request/response pattern in action. The handleRequest constructs a new Response with the body text “Hello worker!”, as well as an explicit 200 status code.
When a Worker receives a fetch event, the script must use event.respondWith to return the newly constructed response to the client. Your Cloudflare Worker script will serve new responses directly from Cloudflare’s edge network instead of continuing to your origin server. A standard server would accept requests and return responses. Cloudflare Workers allows you to respond quickly by constructing responses directly on the Cloudflare edge network.
Build
To build your Slack bot on Cloudflare Workers, you will build up your application file-by-file, separating different parts of the application and using modern JS tooling like ES modules, NPM packages, and async/await functions to put together your application.
The router template includes a class, Router, that is included to help developers with the common task of associating “routes” in your application (for instance, /users, or /about) with “functions”. In this tutorial, there are two routes/function handlers that you need to define:
The
lookupfunction will take requests from Slack (sent when a user uses the/issuecommand), and look up the corresponding issue using the GitHub API. This function will be aPOSTrequest to/lookup.The
webhookfunction will be called when an issue changes on GitHub, via a configured webhook. This function will be aPOSTrequest to/webhook.
Handling requests
Inside of index.js, import the Router class and use it to update the handleRequest function:
index.jsimport { Router } from 'itty-router';
// Create a new router
const router = Router();
router.post("/lookup", lookup);router.post("/webhook", webhook);
router.all("*", () => new Response("404, not found!", { status: 404 }))
addEventListener('fetch', (e) => { e.respondWith(router.handle(e.request))
})
First, import the Router class from itty-router.
The Router class makes use of a few functions to quickly and easily handle requests. The post method takes in a path string and a function handler. This indicates “when a client sends an HTTP POST to the path /lookup, call the lookup function”.
There are two POST routes to handle: /lookup and /webhook. These new routes will point to corresponding functions, lookup and webhook — the two function handlers that you will set up soon.
Once your routes are set up, you need to actually handle the incoming request, which is available under the variable request. The route function on the router takes in a request argument, and returns a response.
If there is no matching route (for example, if someone requests the path /admin), the function should return a response with a status code of 404. router.all catches any unhandled requests and returns a new Response with the body text “404, not found!”, and a status code of 404.
This request/response pattern makes it really straightforward to understand how requests are routed in your Workers application. You are almost done with this file. To complete it, you need to define the corresponding function handlers for your routes. In this tutorial, you will define those handlers in src/handlers:
Create new folders and files$ mkdir -p src/handlers
$ touch src/handlers/lookup.js
$ touch src/handlers/webhook.js
With those files created (you will fill them in soon), import them at the top of index.js. The final version of the code looks like this:
index.jsimport lookup from './src/handlers/lookup';
import webhook from './src/handlers/webhook';
import { Router } from 'itty-router';
// Create a new router
const router = Router();
router.post("/lookup", lookup);router.post("/webhook", webhook);
router.all("*", () => new Response("404, not found!", { status: 404 }))
addEventListener('fetch', (e) => { e.respondWith(router.handle(e.request))
})
Creating the lookup route
In src/handlers/lookup.js, define your first route handler. The lookup handler is a function with one argument, the request being passed from the fetch event in index.js:
src/handlers/lookup.jsexport default async request => {};
To understand how you should design this function, you need to understand how Slack slash commands send data to URLs.
According to the documentation for Slack slash commands, Slack sends an HTTP POST request to your specified URL, with a application/x-www-form-urlencoded content type. For example, if someone were to type /issue cloudflare/wrangler#1, you could expect a data payload in the format:
token=gIkuvaNzQIHg97ATvDxqgjtO&team_id=T0001&team_domain=example&enterprise_id=E0001&enterprise_name=Globular%20Construct%20Inc&channel_id=C2147483705&channel_name=test&user_id=U2147483697&user_name=Steve&command=/issue&text=cloudflare/wrangler#1&response_url=https://hooks.slack.com/commands/1234/5678&trigger_id=13345224609.738474920.8088930838d88f008e0Given this payload body, you need to parse it, and get the value of the text key. With that text, for example, cloudflare/wrangler#1, you can parse that string into known piece of data (owner, repo, and issue_number), and use it to make a request to GitHub’s API, to retrieve the issue data.
With Slack slash commands, you can respond to a slash command by returning structured data as the response to the incoming slash command. In this case, you should use the response from GitHub’s API to present a formatted version of the GitHub issue, including pieces of data like the title of the issue, who created it, and the date it was created. Slack’s new Block Kit framework will allow you to return a detailed message response, by constructing text and image blocks with the data from GitHub’s API.
Parsing slash commands
To begin, parse the incoming data from a Slack message inside of the lookup handler. As previously mentioned, the Slack API sends an HTTP POST in URL Encoded format. To parse this, add the first (and only) NPM package dependency to your project — a popular query string parser package called qs:
Install the qs package$ npm install --save qs
In src/handlers/lookup.js, import qs, and use it to parse the request body, and get the text value from it:
src/handlers/lookup.jsimport qs from 'qs';
export default async request => { const body = await request.text(); const params = qs.parse(body); const text = params['text'].trim();
};
Given a text variable, that contains text like cloudflare/wrangler#1, you should parse that text, and get the individual parts from it for use with GitHub’s API: owner, repo, and issue_number. To do this, create a new file in your application, at src/utils/github.js. This file will contain a number of “utility” functions for working with GitHub’s API. The first of these will be a string parser, called parseGhIssueString:
src/utils/github.jsconst ghIssueRegex = /(?<owner>\w*)\/(?<repo>\w*)\#(?<issue_number>\d*)/;
export const parseGhIssueString = text => { const match = text.match(ghIssueRegex); return match ? match.groups : null;
};
parseGhIssueString takes in a text input, matches it against ghIssueRegex, and if a match is found, returns the groups object from that match, making use of the owner, repo, and issue_number capture groups defined in the regex. By exporting this function from src/utils/github.js, you can make use of it back in src/handlers/lookup.js:
src/handlers/lookup.jsimport qs from 'qs';
import { parseGhIssueString } from '../utils/github';
export default async request => { const body = await request.text(); const params = qs.parse(body); const text = params['text'].trim(); const { owner, repo, issue_number } = parseGhIssueString(text);
};
Making requests to GitHub’s API
With this data, you can make your first API lookup to GitHub. Again, make a new function in src/utils/github.js, to make a fetch request to the GitHub API for the issue data:
src/utils/github.jsconst ghIssueRegex = /(?<owner>\w*)\/(?<repo>\w*)\#(?<issue_number>\d*)/;
export const parseGhIssueString = text => { const match = text.match(ghIssueRegex); return match ? match.groups : null;
};
export const fetchGitHubIssue = (owner, repo, issue_number) => { const url = `https://api.github.com/repos/${owner}/${repo}/issues/${issue_number}`; const headers = { 'User-Agent': 'simple-worker-slack-bot' }; return fetch(url, { headers });
};
Back in src/handlers/lookup.js, use fetchGitHubIssue to make a request to GitHub’s API, and parse the response:
src/handlers/lookup.jsimport qs from 'qs';
import { fetchGitHubIssue, parseGhIssueString } from '../utils/github';
export default async request => { const body = await request.text(); const params = qs.parse(body); const text = params['text'].trim(); const { owner, repo, issue_number } = parseGhIssueString(text);
const response = await fetchGitHubIssue(owner, repo, issue_number); const issue = await response.json();
};
Constructing a Slack message
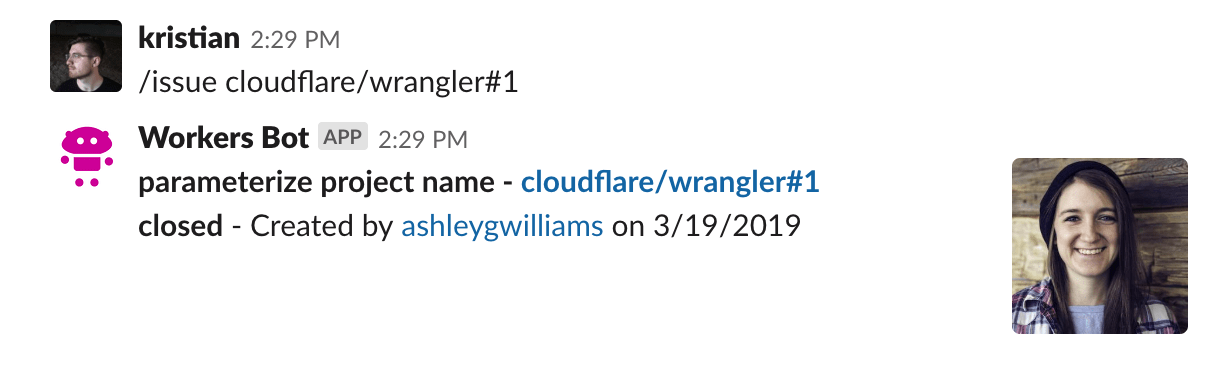
After you have received a response back from GitHub’s API, the final step is to construct a Slack message with the issue data, and return it to the user. The final result will look something like this:

You can see four different pieces in the above screenshot:
- The first line (bolded) links to the issue, and shows the issue title
- The following lines (including code snippets) are the issue body
- The last line of text shows the issue status, the issue creator (with a link to the user’s GitHub profile), and the creation date for the issue
- The profile picture of the issue creator, on the right-hand side
The previously mentioned Block Kit framework will help take the issue data (in the structure lined out in GitHub’s REST API documentation) and format it into something like the above screenshot.
Create another file, src/utils/slack.js, to contain the function constructGhIssueSlackMessage, a function for taking issue data, and turning it into a collection of blocks. Blocks are simple JavaScript objects that Slack will use to format the message:
src/utils/slack.jsexport const constructGhIssueSlackMessage = (issue, issue_string) => { const issue_link = `<${issue.html_url}|${issue_string}>`; const user_link = `<${issue.user.html_url}|${issue.user.login}>`; const date = new Date(Date.parse(issue.created_at)).toLocaleDateString();
const text_lines = [ `*${issue.title} - ${issue_link}*`, issue.body, `*${issue.state}* - Created by ${user_link} on ${date}`, ];
};
Slack messages accept a variant of Markdown, which supports bold text via asterisks (*bolded text*), and links in the format <https://yoururl.com|Display Text>.
Given that format, construct issue_link, which takes the html_url property from the GitHub API issue data (in format https://github.com/cloudflare/wrangler-legacy/issues/1), and the issue_string sent from the Slack slash command, and combines them into a clickable link in the Slack message.
user_link is similar, using issue.user.html_url (in the format https://github.com/signalnerve, a GitHub user) and the user’s GitHub username (issue.user.login), to construct a clickable link to the GitHub user.
Finally, parse issue.created_at, an ISO 8601 string, convert it into an instance of a JavaScript Date, and turn it into a formatted string, in the format MM/DD/YY.
With those variables in place, text_lines is an array of each line of text for the Slack message. The first line is the issue title and the issue link, the second is the issue body, and the final line is the issue state (for example, open or closed), the user link, and the creation date.
With the text constructed, you can finally construct your Slack message, returning an array of blocks for Slack’s Block Kit. In this case, there is only have one block: a section block with Markdown text, and an accessory image of the user who created the issue. Return that single block inside of an array, to complete the constructGhIssueSlackMessage function:
src/utils/slack.jsexport const constructGhIssueSlackMessage = (issue, issue_string) => { const issue_link = `<${issue.html_url}|${issue_string}>`; const user_link = `<${issue.user.html_url}|${issue.user.login}>`; const date = new Date(Date.parse(issue.created_at)).toLocaleDateString();
const text_lines = [ `*${issue.title} - ${issue_link}*`, issue.body, `*${issue.state}* - Created by ${user_link} on ${date}`, ];
return [ { type: 'section', text: { type: 'mrkdwn', text: text_lines.join('\n'), }, accessory: { type: 'image', image_url: issue.user.avatar_url, alt_text: issue.user.login, }, }, ];
};
Finishing the lookup route
In src/handlers/lookup.js, use constructGhIssueSlackMessage to construct blocks, and return them as a new response when the slash command is called:
src/handlers/lookup.jsimport qs from 'qs';
import { fetchGitHubIssue, parseGhIssueString } from '../utils/github';
import { constructGhIssueSlackMessage } from '../utils/slack';
export default async request => { const body = await request.text(); const params = qs.parse(body); const text = params['text'].trim(); const { owner, repo, issue_number } = parseGhIssueString(text);
const response = await fetchGitHubIssue(owner, repo, issue_number); const issue = await response.json();
const blocks = constructGhIssueSlackMessage(issue, text);
return new Response( JSON.stringify({ blocks, response_type: 'in_channel', }), { headers: { 'Content-type': 'application/json' } } );
};
One additional parameter passed into the response is response_type. By default, responses to slash commands are ephemeral, meaning that they are only seen by the user who writes the slash command. Passing a response_type of in_channel, as seen above, will cause the response to appear for all users in the channel.
If you would like the messages to remain private, remove the response_type line. This will cause response_type to default to ephemeral.
Handling errors
The lookup function is almost complete, but there are a number of errors that can occur in the course of this function, such as parsing the body from Slack, getting the issue from GitHub, or constructing the Slack message itself. To address this, wrap the majority of this function in a try/catch block, and return simple error text to the user in Slack if something goes wrong. With that, the final version of src/handlers/lookup.js looks like this:
src/handlers/lookup.jsimport qs from 'qs';
import { fetchGitHubIssue, parseGhIssueString } from '../utils/github';
import { constructGhIssueSlackMessage } from '../utils/slack';
export default async request => { try { const body = await request.text(); const params = qs.parse(body); const text = params['text'].trim(); const { owner, repo, issue_number } = parseGhIssueString(text);
const response = await fetchGitHubIssue(owner, repo, issue_number); const issue = await response.json();
const blocks = constructGhIssueSlackMessage(issue, text);
return new Response( JSON.stringify({ blocks, response_type: 'in_channel', }), { headers: { 'Content-type': 'application/json' } } ); } catch (err) { const errorText = 'Uh-oh! We couldn’t find the issue you provided. We can only find public issues in the following format: `owner/repo#issue_number`.'; return new Response(errorText); }
};
Creating the webhook route
You are now halfway through implementing the route handlers for your Workers application. In implementing the next handler, src/handlers/webhook.js, you will re-use a lot of the code that you have already written for the lookup route.
At the beginning of this tutorial, you configured a GitHub webhook to track any events related to issues in your repository. When an issue is opened, for example, the function corresponding to the path /webhook on your Workers application should take the data sent to it from GitHub, and post a new message in the configured Slack channel.
In src/handlers/webhook.js, define an async function that takes in a request, and make it the default export for this file:
src/handlers/webhook.jsexport default async request => {};
Much like with the lookup function handler, you will need to parse the incoming payload inside of request, get the relevant issue data from it (refer to the GitHub API documentation on IssueEvent for the full payload schema), and send a formatted message to Slack to indicate what has changed. The final version will look something like this:
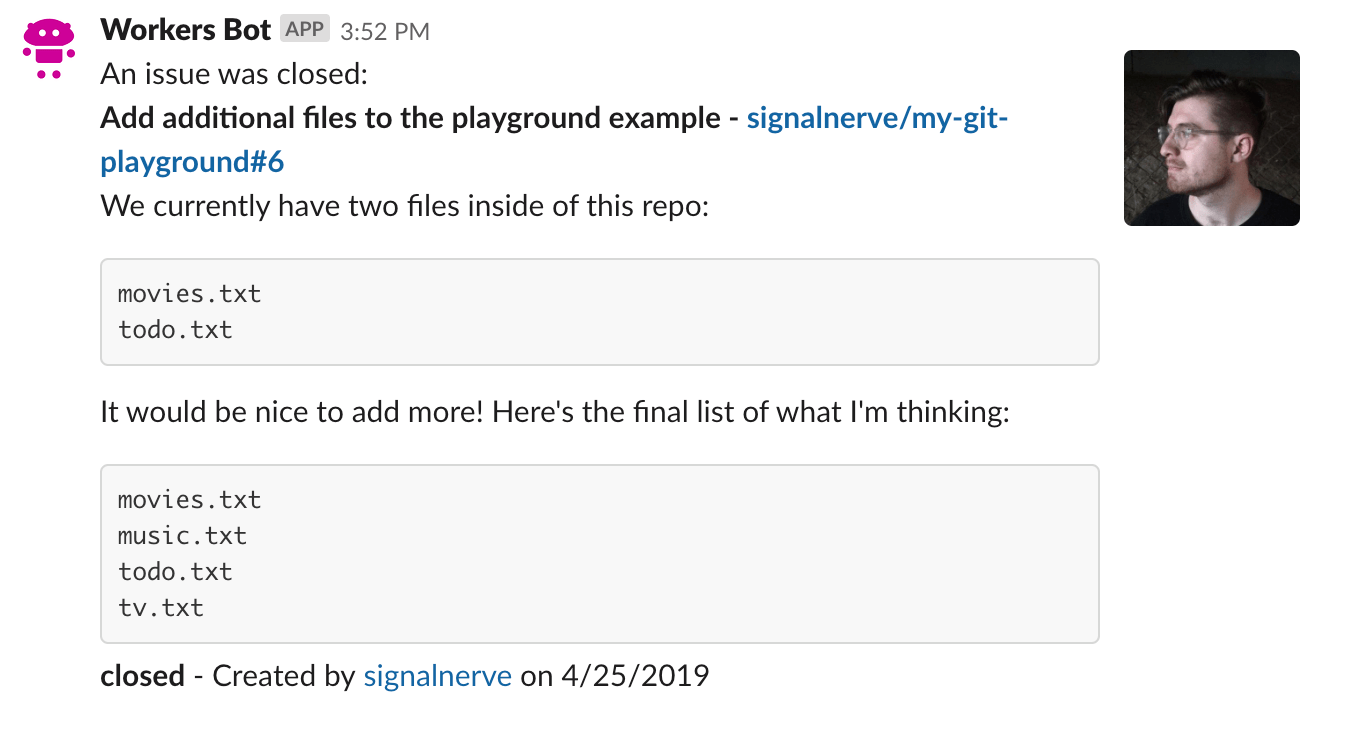
Compare this message format to the format returned when a user uses the /issue slash command. You will see that there is only one actual difference between the two: the addition of an action text on the first line, in the format An issue was $action:. This action, which is sent as part of the IssueEvent from GitHub, will be used as you construct a very familiar looking collection of blocks using Slack’s Block Kit.
Parsing event data
To start filling out the function, take in the request body, parse it into an object, and construct some helper variables:
src/handlers/webhook.jsimport { constructGhIssueSlackMessage } from '../utils/slack';
export default async request => { const body = await request.text(); const { action, issue, repository } = JSON.parse(body); const prefix_text = `An issue was ${action}:`; const issue_string = `${repository.owner.login}/${repository.name}#${issue.number}`;
};
An IssueEvent, the payload sent from GitHub as part of your webhook configuration, includes an action (what happened to the issue: for example, it was opened, closed, locked, etc.), the issue itself, and the repository, among other things.
Use JSON.parse to convert the payload body of the request from JSON into a plain JS object. Use ES6 destructuring to set action, issue and repository as variables you can use in your code. prefix_text is a simple string indicating what happened to the issue, and issue_string is the familiar string owner/repo#issue_number that you have seen before: while the lookup handler directly used the text sent from Slack to fill in issue_string, you will construct it directly based on the data passed in the JSON payload.
Constructing and sending a Slack message
The messages your Slack bot sends back to your Slack channel from the lookup and webhook function handlers are incredibly similar. Because of this, you can re-use the existing constructGhIssueSlackMessage to continue populating src/handlers/webhook.js. Import the function from src/utils/slack.js, and pass the issue data into it:
src/handlers/webhook.jsimport { constructGhIssueSlackMessage } from '../utils/slack';
export default async request => { const body = await request.text(); const { action, issue, repository } = JSON.parse(body); const prefix_text = `An issue was ${action}:`; const issue_string = `${repository.owner.login}/${repository.name}#${issue.number}`; const blocks = constructGhIssueSlackMessage(issue, issue_string, prefix_text);
};
Importantly, the usage of constructGhIssueSlackMessage in this handler adds one additional argument to the function, prefix_text. Update the corresponding function inside of src/utils/slack.js, adding prefix_text to the collection of text_lines in the message block, if it has been passed in to the function.
Add a simple utility function, compact, which takes an array, and filters out any null or undefined values from it. This function will be used to remove prefix_text from text_lines if it has not actually been passed in to the function, such as when called from src/handlers/lookup.js. The full (and final) version of the src/utils/slack.js looks like this:
src/utils/slack.jsconst compact = array => array.filter(el => el);
export const constructGhIssueSlackMessage = (issue, issue_string, prefix_text) => { const issue_link = `<${issue.html_url}|${issue_string}>`; const user_link = `<${issue.user.html_url}|${issue.user.login}>`; const date = new Date(Date.parse(issue.created_at)).toLocaleDateString();
const text_lines = [ prefix_text, `*${issue.title} - ${issue_link}*`, issue.body, `*${issue.state}* - Created by ${user_link} on ${date}`, ];
return [ { type: 'section', text: { type: 'mrkdwn', text: compact(text_lines).join('\n'), }, accessory: { type: 'image', image_url: issue.user.avatar_url, alt_text: issue.user.login, }, }, ];
};
Back in src/handlers/webhook.js, the blocks that are returned from constructGhIssueSlackMessage become the body in a new fetch request, an HTTP POST request to a Slack webhook URL. Once that request completes, return a response with status code 200, and the body text "OK":
src/handlers/webhook.jsimport { constructGhIssueSlackMessage } from '../utils/slack';
export default async request => { const body = await request.text(); const { action, issue, repository } = JSON.parse(body); const prefix_text = `An issue was ${action}:`; const issue_string = `${repository.owner.login}/${repository.name}#${issue.number}`; const blocks = constructGhIssueSlackMessage(issue, issue_string, prefix_text);
const postToSlack = await fetch(SLACK_WEBHOOK_URL, { body: JSON.stringify({ blocks }), method: 'POST', headers: { 'Content-Type': 'application/json' }, });
return new Response('OK');
};
The constant SLACK_WEBHOOK_URL represents the Slack Webhook URL that you created all the way back in the Incoming Webhook section of this tutorial.
To use this constant inside of your codebase, use the wrangler secret command:
Set the SLACK_WEBHOOK_URL secret$ wrangler secret put SLACK_WEBHOOK_URLEnter the secret text you’d like assigned to the variable name on the script named slack-bot-ENVIRONMENT_NAME: https://hooks.slack.com/services/abc123 Handling errors
Similarly to the lookup function handler, the webhook function handler should include some basic error handling. Unlike lookup, which sends responses directly back into Slack, if something goes wrong with your webhook, it may be useful to actually generate an erroneous response, and return it to GitHub.
To do this, wrap the majority of the webhook function handler in a try/catch block, and construct a new response with a status code of 500, and return it. The final version of src/handlers/webhook.js looks like this:
src/handlers/webhook.jsimport { constructGhIssueSlackMessage } from '../utils/slack';
export default async request => { try { const body = await request.text(); const { action, issue, repository } = JSON.parse(body); const prefix_text = `An issue was ${action}:`; const issue_string = `${repository.owner.login}/${repository.name}#${issue.number}`; const blocks = constructGhIssueSlackMessage(issue, issue_string, prefix_text);
const postToSlack = await fetch(SLACK_WEBHOOK_URL, { body: JSON.stringify({ blocks }), method: 'POST', headers: { 'Content-Type': 'application/json' }, });
return new Response('OK'); } catch (err) { const errorText = 'Unable to handle webhook'; return new Response(errorText, { status: 500 }); }
};
Publish
By completing the preceding steps, you have finished writing the code for your Slack bot. You can now publish your application.
Wrangler has built-in support for bundling, uploading, and releasing your Cloudflare Workers application. To do this, run wrangler publish, which will build and publish your code:
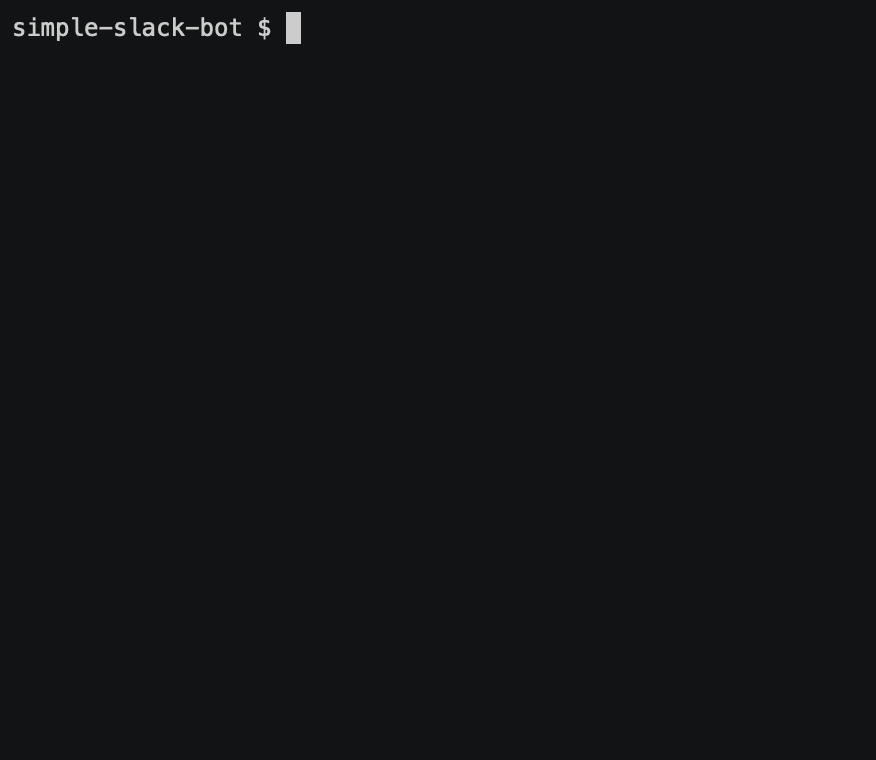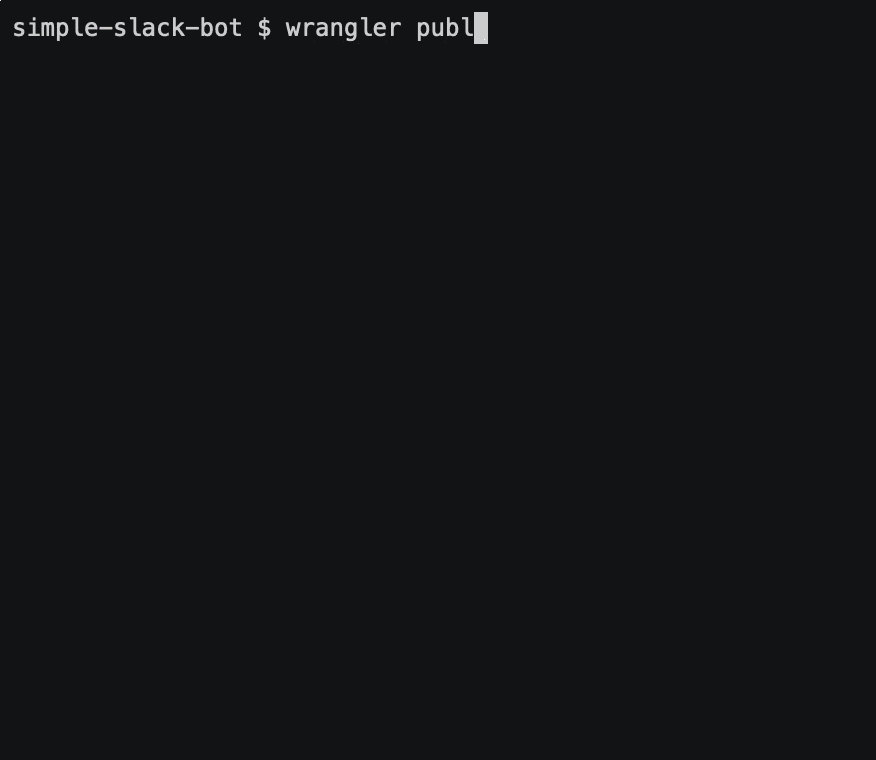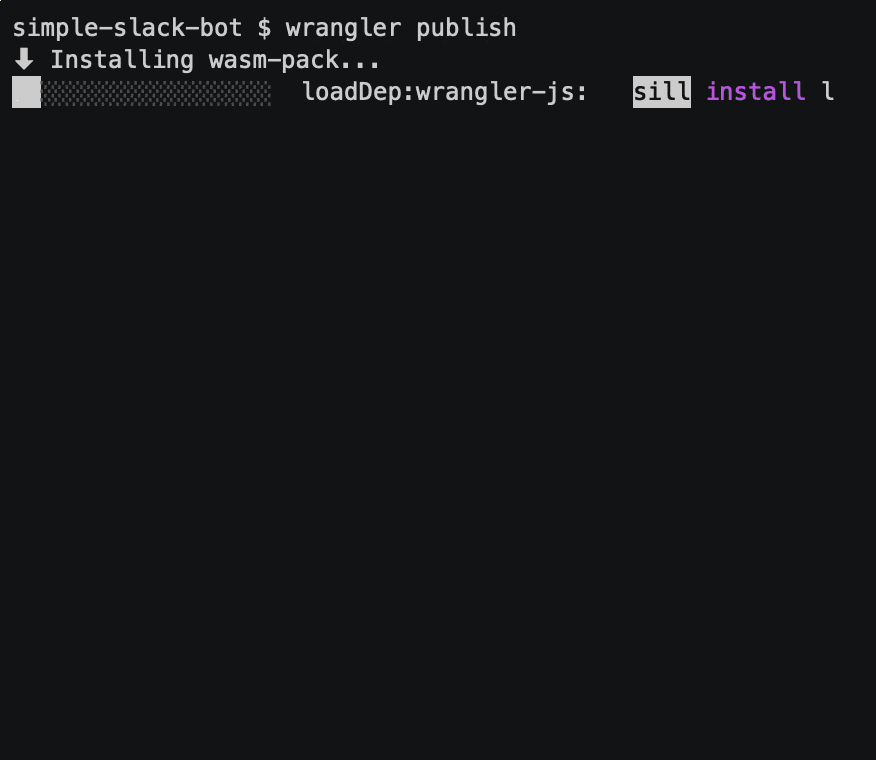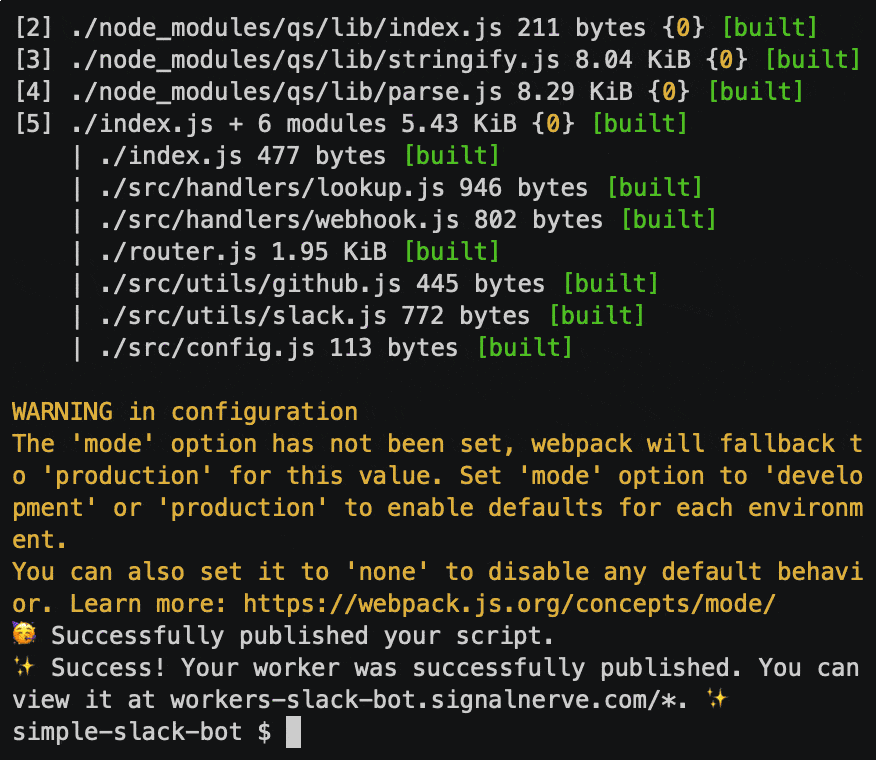
Publishing your Workers application should now cause issue updates to start appearing in your Slack channel, as the GitHub webhook can now successfully reach your Workers webhook route:
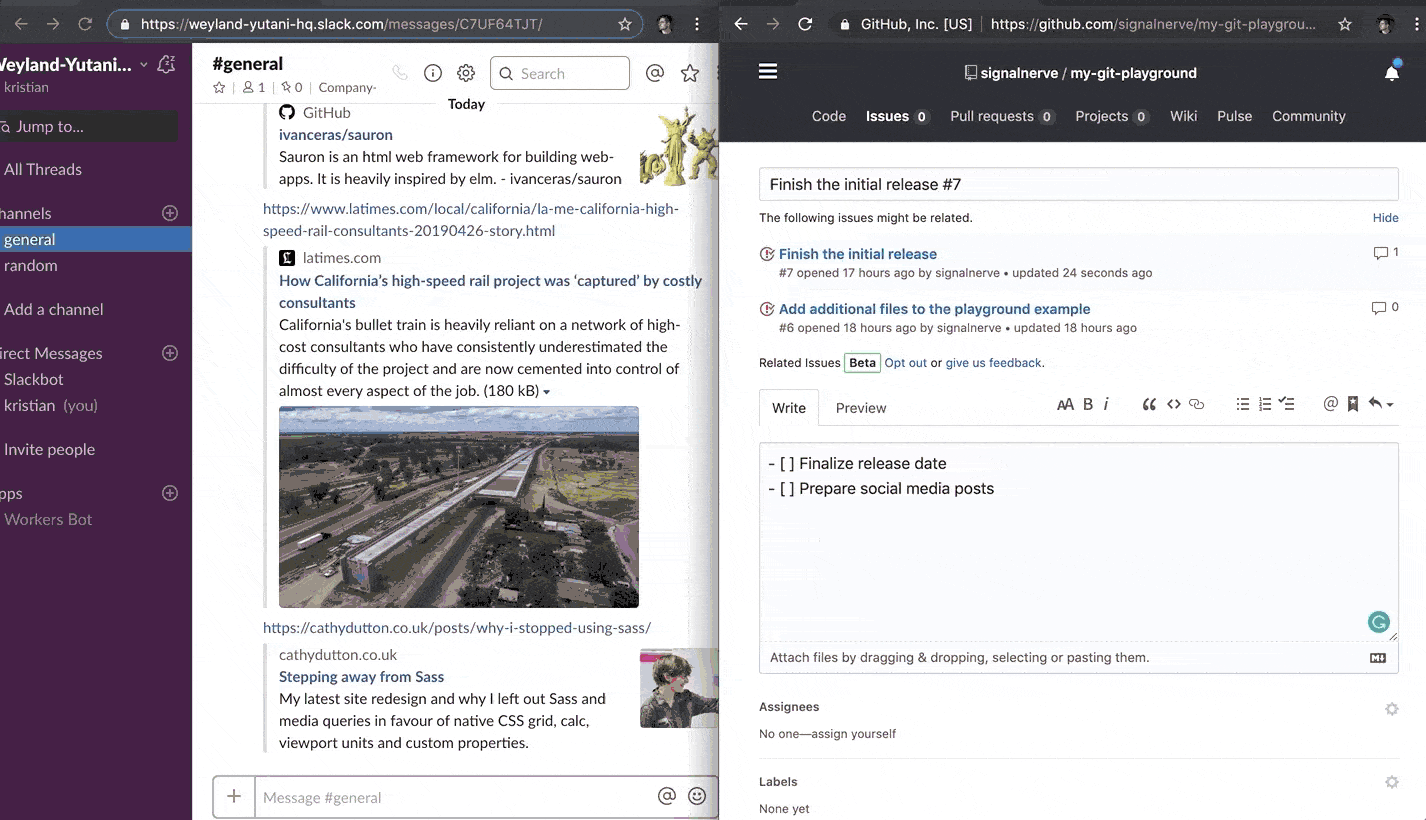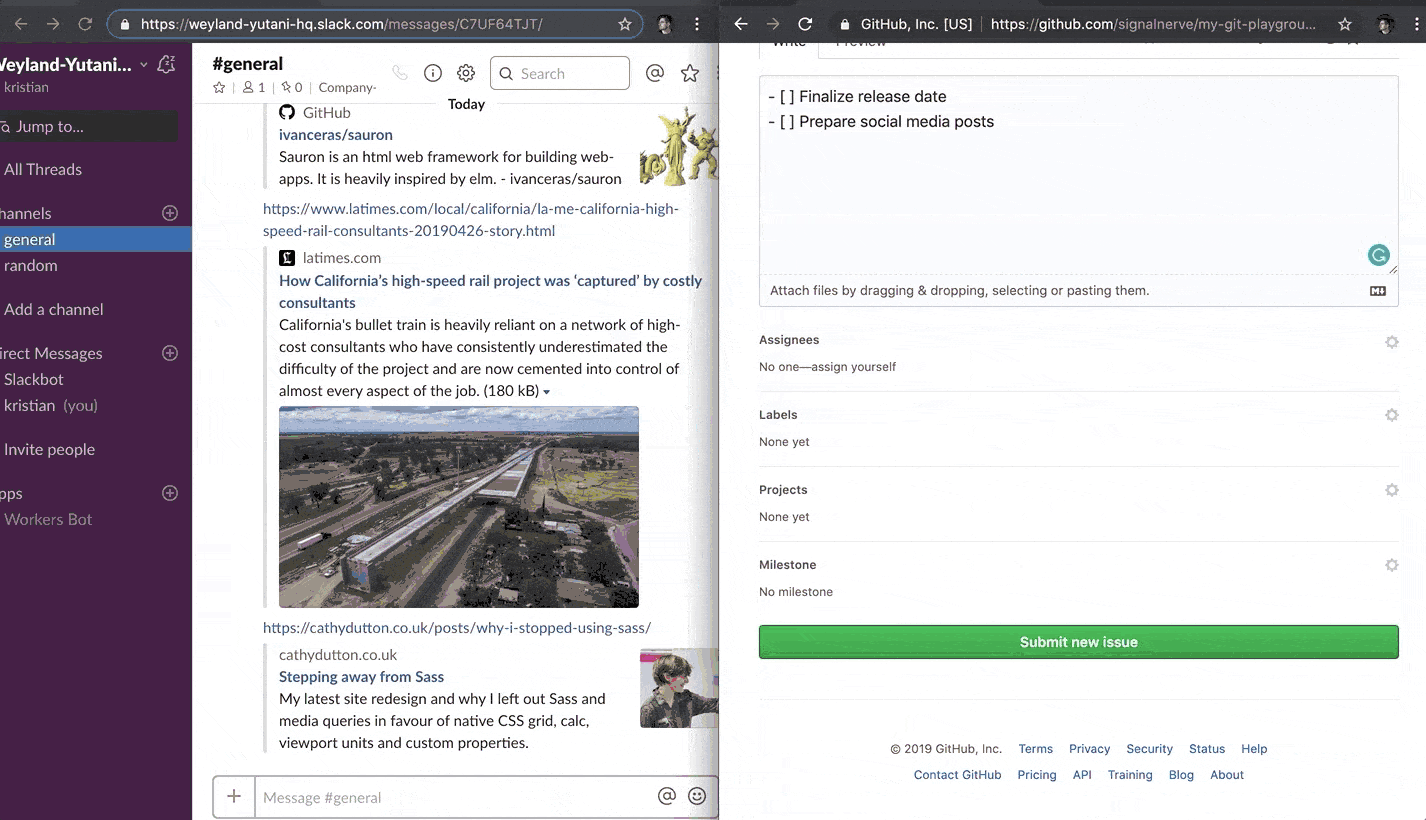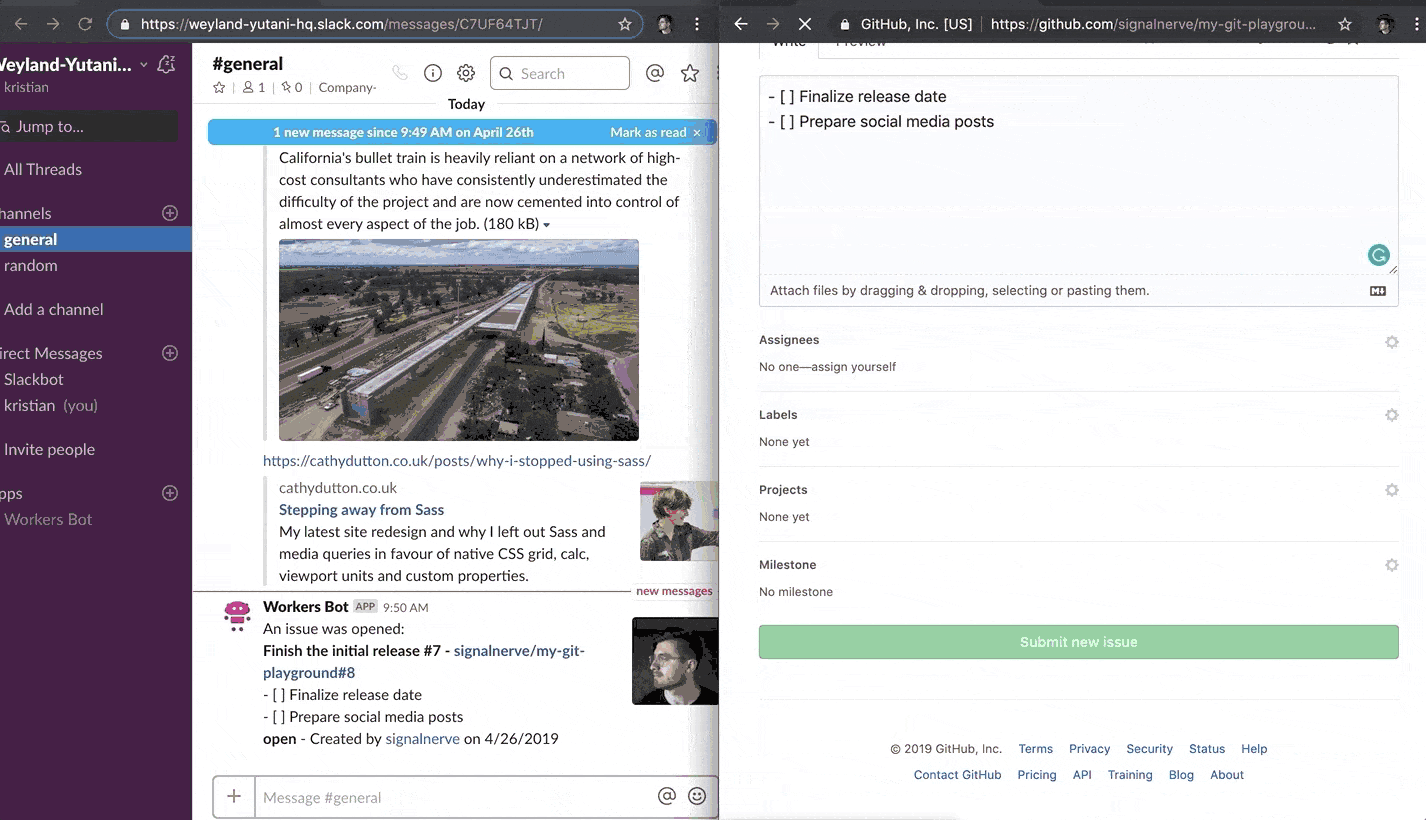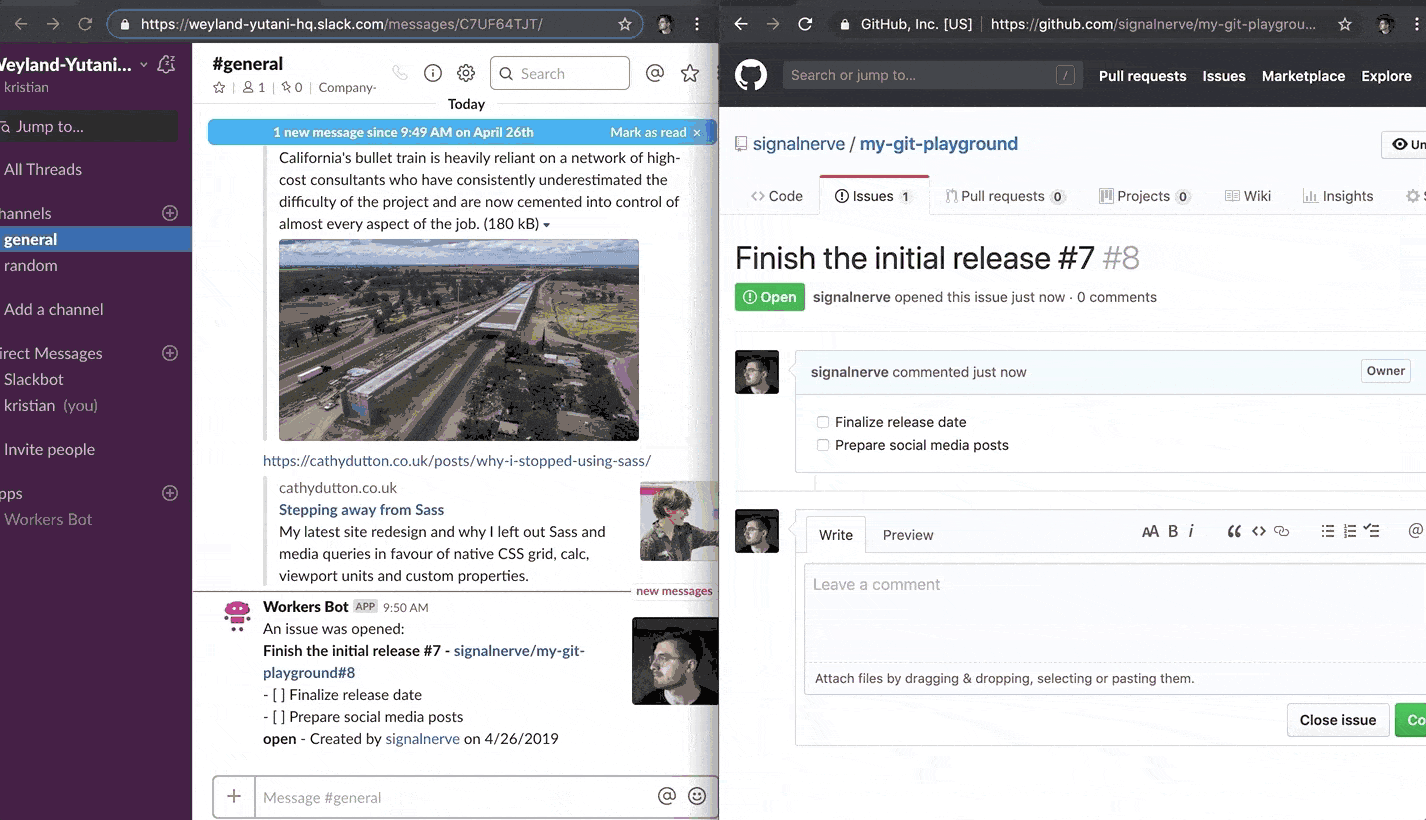
Related resources
In this tutorial, you built and published a Cloudflare Workers application that can respond to GitHub webhook events, and allow GitHub API lookups within Slack. If you would like to review the full source code for this application, you can find the repository on GitHub.
If you want to get started building your own projects, review the existing list of Quickstart templates.