How authenticated origin pulls work
Simple explanation
When visitors request content from your domain, Cloudflare first attempts to serve content from the cache. Failing that, Cloudflare sends a request — or an origin pull — back to your origin web server to get the content.
Authenticated origin pulls make sure that all of these origin pulls come from Cloudflare. Put another way, authenticated origin pulls ensure that any HTTPS requests outside of Cloudflare will not receive a response from your origin.
Detailed explanation
Cloudflare enforces authenticated origin pulls by adding an extra layer of TLS client certificate authentication when connecting between Cloudflare and the origin web server.
For more details, refer to the introductory blog post.
Types of handshakes
For more details, refer to What is a TLS handshake?.
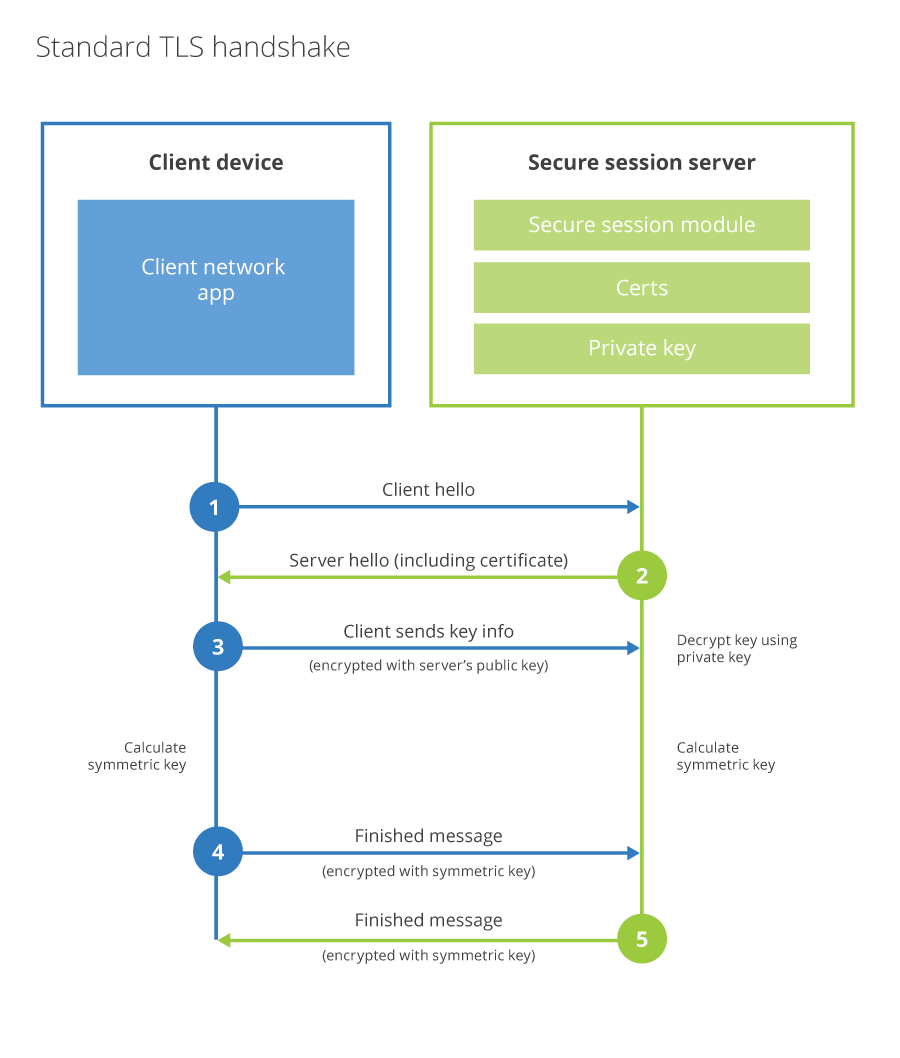
Standard TLS handshake
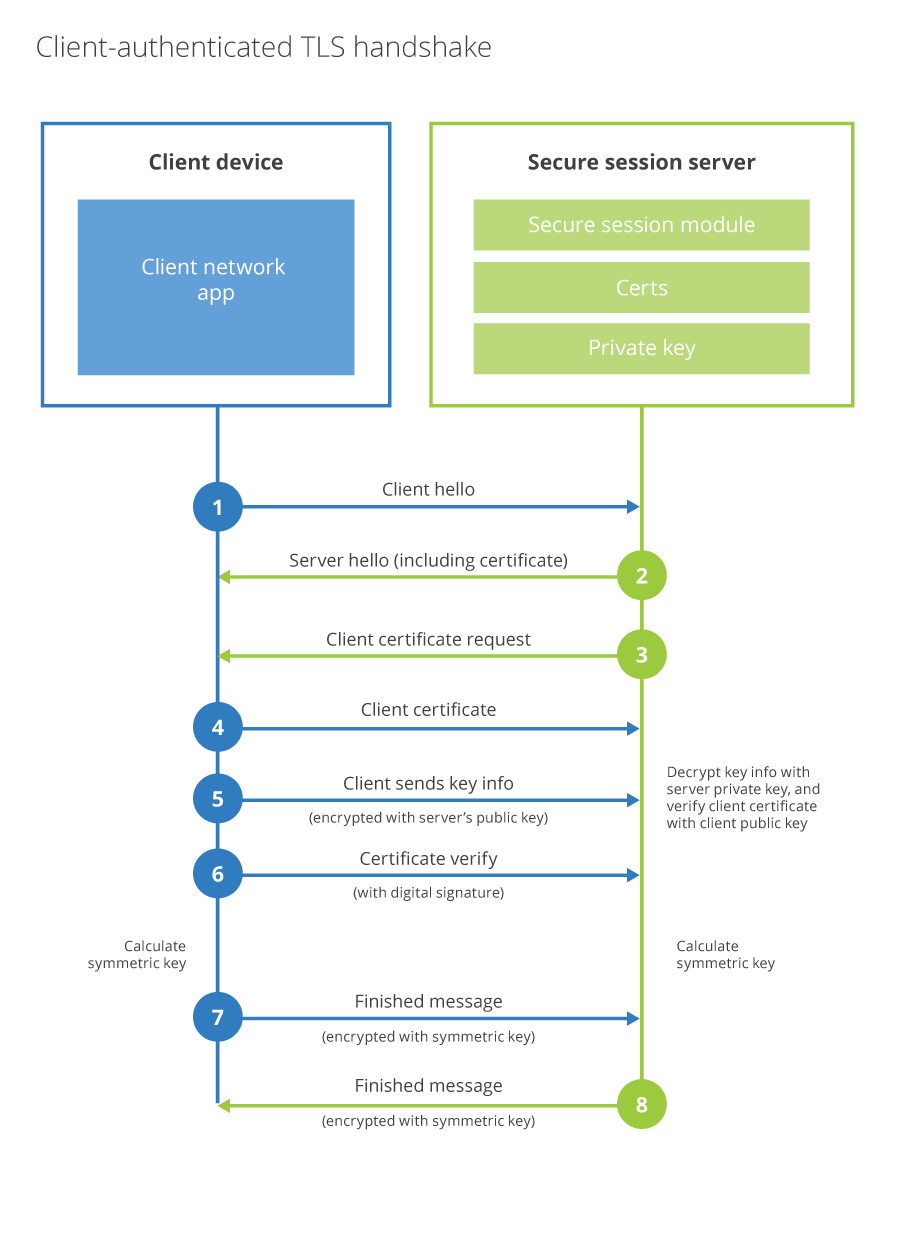
Client authenticated TLS handshake
Comparison diagrams
Without authenticated origin pulls - and even with Full or Full (strict) encryption modes - Cloudflare performs standard TLS handshakes between a client device and Cloudflare and Cloudflare and your origin.
This lack of authentication means that - even if your origin is protected behind Cloudflare - attackers with your origin’s IP address will still receive a response from your origin for HTTPS requests.
With authenticated origin pulls, Cloudflare performs standard TLS handshakes between a client device and Cloudflare, but a client-authenticated TLS handshake between Cloudflare and your origin.
This additional layer of authentication ensures that any HTTPS requests outside of Cloudflare will not receive a response from your origin.